Shapes of Diamonds
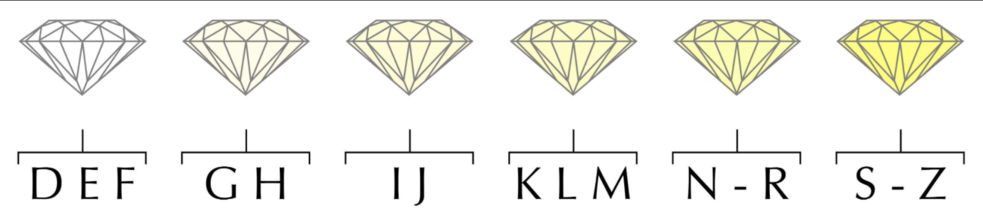
When buying diamonds, their colour is one of the most critical aspects that shouldn't be overlooked because one of the important aspects for pricing it is its colour.Diamonds can be either colourless (white) or fancy-coloured (coloured).Diamond colour is a product of the diamond creation process.A diamond's colour refers to its transparency, or how clear it is. While the colourless diamonds are of the highest clarity, the lower quality has a tint in them. Colourless diamonds are of significant importance. They are chemically pure and contain little to no impurities. As the diamond shows more tint of colour, it goes down the grading scale.
Diamonds are also graded as Fancy Colour, which uses a distinctive set of conditions. With fancy colour diamonds, the rarest and most valuable colours are saturated pinks, blues, and greens. Very slight colour differences can have a huge impact on its value. Compared to fancybrowns, diamonds with a noticeable hint of any other hue are considerably rarer. Even in light tones and weak saturation, they qualify as fancy colours. Red, green, and blue diamonds with medium to dark tones and moderate saturations are extremely rare.
While grading white diamonds is binary (colour or not), it’s much more complex with fancy-colored stones. Fancy diamonds are graded by not one but three features. Hue (the colour name or mix), tone (light or dark colour), and saturation (how intense or strong the colour is).It takes a complex and specialised process to grade fancy colour diamonds. It also involves highly trained laboratory graders to complete the process accurately.
So when buying diamonds, should one consider the colour?
Indeed yes. But there are other parameters to consider as well. The quality of a diamond is judged based on 4 Cs- Cut, colour, clarity and carat.
Read other blogs to know about the different Cs of diamond grading.
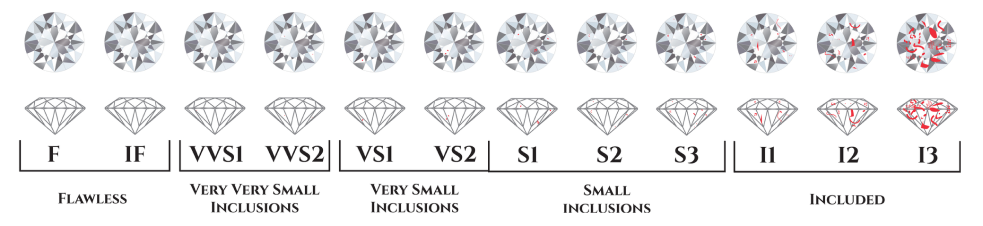
With fancy color diamonds, color is the dominant value factor. Even diamonds with numerous inclusions that result in a low clarity grade are prized by connoisseurs if they display attractive face-up color. Of course, inclusions that threaten the gem’s durability can lower a fancy color diamond’s value significantly. Fancy color diamonds can exhibit color graining, which is considered an inclusion
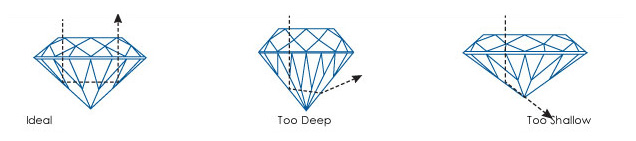
Diamond colour is largely influenced by its size and shape. The larger a diamond is, or the deeper its pavilion, the farther light can travel in it, giving a richer, more intense colour.
Cuts are also an important consideration when buying a diamond because the diamond shape is the first thing that gets noticed.
Have a read at different diamond shapes.
1. Round Diamonds:
The most popular diamond shape, round diamonds comprises 75% of the total diamonds sold. It is largely preferred because of its 360-degree symmetry in form, capability to reflect more light and maximum brightness.
2. Princess-cut Diamonds:
This much-loved fancy shape combines the dynamism of a round diamond and the classiness of an emerald-cut or princess-cut diamond. Largely used in engagement rings, it is a great choice for different styles because of its flexibility.
3. Marquise Diamonds:
With two sharp points on either end, Marquise-cut diamonds are sleek in their form. Since it accentuates long, the marquise diamond has one of the largest surface areas of any diamond shape, making it a good choice when trying to maximize perceived size.
4. Oval Diamonds:
These are brilliantly modified versions of round diamonds. Oval diamonds exhibit uniqueness with their slightly elongated structure, creating the illusion of greater size.

It is the most noticeable quality of a diamond. Diamonds and other gemstones are measured using a unit called metric carats. Carat, i.e., “ct” measures the weight of a diamond. One carat equals 0.2 or one-fifth of a gram. That means five carats equals one gram.
Sparking Sustainability with Lab-Grown Diamonds: An Introduction
Lab-grown diamonds are getting popular a responsible approach towards their creation. They are very similar to natural diamonds - the only difference being the way in which they are made. Lab-grown diamonds are sustainably created using technology. Whereas, natural diamonds are formed over billions of years under the earth's crust. Another point to note would be that lab-grown diamonds can be grown in a matter of weeks in the laboratory. It is far-fetched to spot a difference between lab-grown and natural diamonds, for they are rather identical in composition, shine and radiance. Despite being similar, lab-grown diamonds follow an ethical and eco-friendly process, unlike natural diamonds.
Let's dig deep into how Diamonds are formed!
Diamonds are simply made of just one element, Carbon. That’s right a diamond is usually made of just carbon atoms that are crystallized due to the intense heat and pressure conditions within the earth’s crust. A lab-grown diamond is made by replicating these conditions using advanced technologies and take just several weeks and not millions of years to form. Lab-grown diamonds are man-made diamonds that have the same optical and chemical characteristics as a mined diamond. This means one cannot tell them apart with the naked eye, even for a professional diamond grader.
Currently, there are only two methods used to form lab-grown diamonds; HPHT (High pressure, High Temperature) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition).
Both methods begin with a small piece of diamond, which is known as the seed. This seed is then placed inside the chamber where the conditions of the earth’s crust are replicated.
HPHT places intense heat which is usually around 1,500 degrees Celsius and immense pressure close to around 1.5 million pounds per square inch on the diamond seed.
CVD uses less heat and pressure as compared to the HPHT method and instead uses plasma technology to break down different mixtures of gases that break down and harden into crystalized carbon atoms which then stick to the diamond seed.
Properties of Lab-Grown Diamonds:
- Conflict-free, Ethically Sourced and Sustainable:
Created in a controlled lab environment, they exert a lower impact on the environment, as compared to the natural diamonds derived through mining.
- Value for Money:
Lab-Grown Diamonds are more pocket friendly, offering brilliance and shine just like the natural ones.
- Stone Cut and Shape:
Lab-Grown Diamonds offer greater versatility in terms of their structure, while natural diamonds are constrained by their intrinsic shape.
Bhavani Lab-Grown Diamonds presents lab-created diamonds, crafted with honesty and polished to shine. They are created inside a laboratory following sophisticated processes by proficiently skilled experts. We assure you that these sparkles glow as true and authentic as the natural ones.
The process of creating Lab-Grown Diamonds!
Lab-Grown Diamonds are redefining the gems and jewellery industry with a sustainable and ethical approach towards their creation. Let us understand this intricate process.
1. Diamond seeds' Inspection and Placement:
Each diamond seed is carefully evaluated to eliminate imperfections. The best seeds are then carefully placed on a metal disk to be placed inside the diamond-growing equipment. They are generally created using 2 processes: High-Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
2. Exposed to high temperatures:
A combination of high temperature, pressure and gases create a setting that enables carbon atoms to break down and fall upon the seeds inside the chamber. With time, the seeds transform into rough diamonds within a few weeks.
3. Cut, Polish, Shine:
The rough diamonds produced acquire the same chemical, physical and optical properties as mined diamonds, through this process. They are then carefully cut and polished to yield a genuine, authentic and beautifully cultivated diamond.
We at Bhavani, have studied lab-grown diamonds extensively over the past few years, and to make a positive impact on the environment, we endeavour to provide the finest quality of lab-grown diamonds.